Orphan Page: Why It Hurts Your Link Building

Search engines discover the vast majority of web pages through internal links, with Google's crawlers following links as their primary discovery mechanism, yet most SEO professionals only stumble upon orphan pages by accident during routine audits. These disconnected pages represent one of the most underestimated threats to organic visibility, quietly bleeding link equity and hiding valuable content from both crawlers and users.
The problem runs deeper than simple technical oversight. Enterprise websites lose an average of 15-25% of their indexable pages to orphan status during major migrations, platform changes, or restructuring initiatives. Research indicates that websites with well-structured internal linking profiles exhibit 21% higher conversion rates compared to those with poor link structures, demonstrating the business impact of proper page connectivity.
What makes this particularly frustrating is how these pages continue generating server resources and hosting costs while contributing nothing to organic performance. You're essentially paying to host invisible content that your competitors can easily outrank with properly connected alternatives.
Understanding orphan pages beyond the textbook definition
An orphan page is a web page that is not linked to by any other pages on a website, but this standard definition misses several critical nuances that impact how we detect and address them in practice.
True orphan pages exist in complete isolation from your site's internal link architecture. However, the term often gets applied loosely to pages with minimal internal linking or those accessible only through deep navigation paths. This distinction matters because different isolation levels require different strategic approaches.
I've found that partial orphans, pages with only one or two internal links from low-authority sections, often perform almost as poorly as complete orphans in search results. These quasi-orphaned assets demonstrate how internal link distribution affects page authority distribution across your domain.
The spectrum of orphan page types
Complete orphans have zero internal links pointing to them from anywhere on your domain. These pages typically emerge from content management system glitches, broken migration processes, or manual publishing errors that bypass normal workflow checks.
Functional orphans maintain technical connectivity but exist outside meaningful user pathways. These pages might be linked from outdated sitemaps, hidden footer sections, or archived category pages that receive no traffic or crawl attention.
Temporary orphans lose their connections during routine maintenance, server updates, or content management system changes. These pages often reconnect automatically once systems restore, but the temporary disconnection can impact rankings if it occurs during critical crawl periods.
Strategic orphans are intentionally isolated for specific business reasons. These might include internal tool documentation, private landing pages for email campaigns, or beta testing environments that shouldn't appear in public search results.
Why orphan pages matter in your link-building strategy
Orphan pages can seriously undermine your SEO and user engagement. When crawlers can’t find these pages through your normal navigation, they miss out on valuable authority, and users never get to discover the content you’ve worked hard to create.
Missed authority and visibility
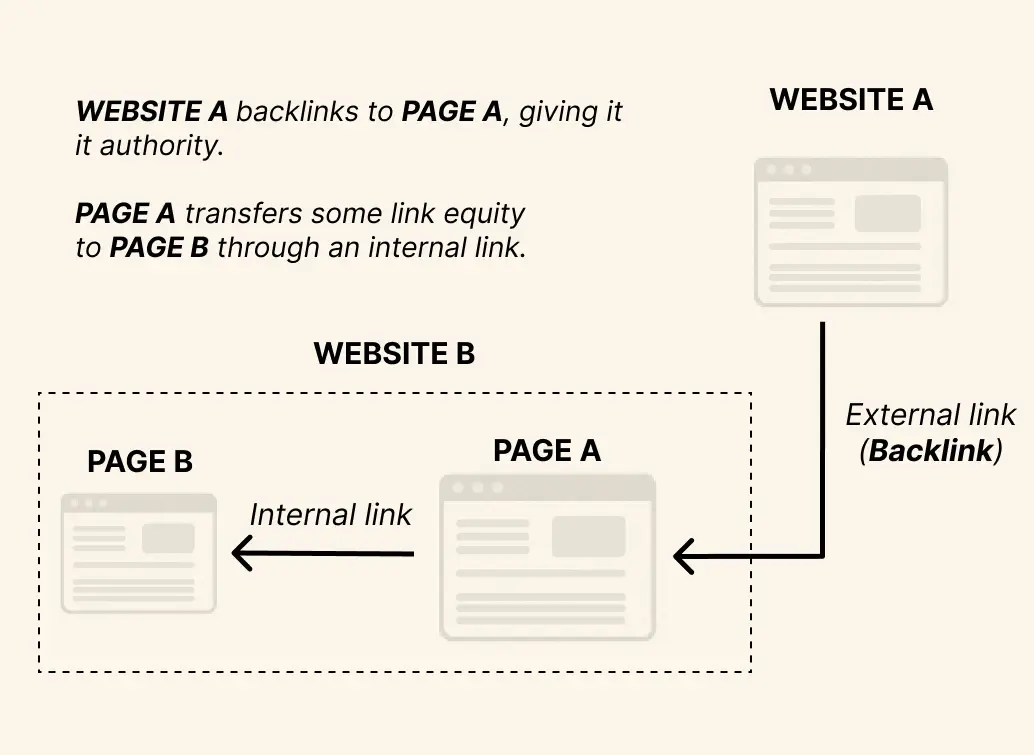
Even if you build external backlinks to an orphan page, it remains disconnected from the rest of your site’s hierarchy. Without internal links to channel “link juice,” that page won’t fully benefit from your site’s overall authority, and crawlers may still treat it as a lower-priority URL.
Untapped link-building opportunities
An audit to identify orphan pages reveals high-potential candidates that have been overlooked. Once you know they exist, you can weave them into your content map—linking from relevant, high-authority pages—to amplify topical relevance and ensure every backlink you earn counts for more.
Improved crawl efficiency
Too many orphan pages clogs your crawl budget, diverting Googlebot away from priority URLs. By integrating orphans into your internal linking structure (or pruning them if outdated), you create a cleaner, more logical site architecture that benefits both search engines and visitors.
Addressing orphan pages turns forgotten content into SEO assets. By interlinking, redirecting, or consolidating these pages, you’ll not only rescue valuable content but also boost the impact of your entire link-building effort.
The crawling and indexing mechanics behind orphan page discovery
Search engine crawlers use internal links as their primary discovery mechanism, but they maintain multiple pathways for finding content. Understanding these mechanisms helps explain why some orphan pages still get indexed while others disappear completely.
The biggest SEO issue orphan pages have is that crawlers will definitely not find that page with the most reliable page-finding method search engines use — following links. This reliability factor means that even pages discoverable through alternative methods receive lower priority in crawl schedules and index updates.
XML sitemaps provide a secondary discovery path, but crawler behavior suggests they treat sitemap-only pages with skepticism. Pages that appear in sitemaps but lack internal link support often experience delayed indexing, reduced crawl frequency, and lower authority scores.
Server log analysis reveals that orphan pages receiving direct traffic through bookmarks, external links, or manual URL entry maintain better search engine attention than those with zero visit history. This suggests that user engagement signals partially compensate for internal link deficits.
Authority distribution and orphan page performance
PageRank and similar authority algorithms require link connectivity to function properly. Orphan pages essentially operate outside these systems, regardless of their content quality or relevance to user queries.
In my experience testing authority recovery for previously orphaned pages, those reconnected with strategic internal links from high-authority sections can recover 60-80% of their original ranking positions within 2-3 months. However, pages left orphaned for extended periods often require additional optimization beyond simple reconnection.
The authority isolation effect compounds over time. While newly orphaned pages might maintain some ranking momentum through cached signals, long-term orphans typically slide out of competitive result positions entirely.
Link equity that would normally flow through these pages gets redistributed to other site sections, potentially creating authority imbalances that affect overall domain performance. This redistribution isn't automatically reversed when orphan pages reconnect, requiring additional internal link optimization to restore optimal equity flow.
Advanced detection methodologies for enterprise-scale audits
Standard crawling tools only reveal orphan pages when they can access complete URL inventories from external sources. This limitation means traditional detection methods miss significant portions of orphaned content on large, complex websites.
Multi-source detection strategies
One of the best places to start looking for orphan pages is your own Google Analytics data (or any other analytics packages you use). Analytics data provides historical evidence of pages that once received traffic but no longer appear in crawl results. Internal links contribute to better user experience, higher conversion rates, and more efficient website crawling, making their absence particularly problematic for business performance.
Server log analysis offers the most comprehensive orphan detection capability because it captures every URL request regardless of internal link status. Combining log file data with crawl results reveals the full scope of orphaned content across your domain.
Search Console performance data frequently contains orphan pages that still rank for branded queries or long-tail keywords. These pages often maintain minimal visibility through cached authority or direct URL recognition, making them valuable recovery targets.
Database queries against content management systems can uncover published pages that never received proper internal link integration. This approach is particularly effective for large publishing platforms where automated workflows might skip linking steps.
Automated detection and monitoring systems
Enterprise SEO requires automated systems that continuously monitor for new orphan pages rather than relying on periodic manual audits. Most orphan page problems are time-sensitive, where quick detection and resolution prevent ranking losses.
Custom scripts that compare sitemap contents against crawl results provide ongoing orphan detection for sites with reliable sitemap maintenance. However, this approach fails when sitemaps themselves contain errors or outdated URLs.
Integration between content management systems and SEO tools enables real-time orphan detection during the publishing process. This preventive approach stops orphan pages from emerging rather than fixing them after problems develop.
Machine learning models can predict orphan page risk based on publishing patterns, content types, and historical link integration data. These predictive systems help prioritize manual review resources on high-risk content before orphan status occurs.
Strategic approaches to orphan page recovery and prevention
Not every orphan page deserves reconnection to your main site architecture. Recovery strategies must balance potential SEO value against site organization and user experience considerations.
Value assessment frameworks
Traffic history analysis helps prioritize orphan pages with demonstrated performance potential. Pages that previously drove significant organic traffic or conversions typically justify recovery efforts even if they've been orphaned for extended periods.
Content uniqueness and competitive advantage determine whether orphan pages merit integration or replacement. High-quality, differentiated content usually deserves recovery, while thin or duplicate content might be better consolidated or removed entirely.
Technical performance factors including page speed, mobile optimization, and security compliance affect recovery priority. Orphan pages with significant technical debt often require comprehensive updates beyond simple reconnection.
Brand alignment and message consistency influence recovery decisions for marketing and promotional content. Orphaned pages containing outdated positioning or discontinued product information might cause brand confusion if simply reconnected without content updates.
Internal linking integration strategies
Strategic internal linking goes beyond basic reconnection to optimize authority flow and user journey integration. Effective orphan page recovery requires understanding how reconnected content fits into broader site architecture and conversion pathways.
Topical clustering approaches group recovered orphan pages with related content through strategic internal links. This method helps search engines understand content relationships while creating natural user navigation paths between previously isolated pages.
Authority scaffolding involves connecting high-value orphan pages to established authority pages through intermediate linking structures. This approach helps recovered pages benefit from existing domain authority while building their own link equity over time.
User journey integration ensures that recovered orphan pages serve legitimate user needs rather than existing solely for SEO purposes. Pages that don't fit natural user workflows often perform poorly even after technical reconnection.
Prevention systems and governance
Organizational processes prevent orphan pages more effectively than technical solutions alone. Most orphan page problems stem from workflow issues rather than system limitations, requiring operational changes to achieve lasting improvement.
Content governance frameworks establish clear ownership and maintenance responsibilities for different content types and site sections. Without clear accountability, orphan pages inevitably reappear even after comprehensive cleanup efforts.
Publishing workflow integration builds orphan prevention directly into content creation processes. Automated checks during content approval and publication stages can prevent orphan pages from going live initially.
Regular audit scheduling ensures ongoing orphan detection before problems compound. However, audit frequency must balance thoroughness against resource requirements, particularly for large enterprise websites.
Technical implementation and tool optimization
Professional-grade orphan page management requires sophisticated tooling that goes beyond basic crawler functionality. Enterprise SEO teams need integrated systems that combine detection, analysis, and resolution capabilities.
Crawling optimization for orphan detection
Connect to Google Analytics and Search Console, integrate XML Sitemaps and discover orphan pages, that are not linked to internally from the website. This multi-source approach provides more complete orphan detection than single-method scanning, as Google can only crawl links if they're properly formatted HTML anchor elements with href attributes.
Crawl budget optimization becomes critical when dealing with large numbers of potential orphan pages. Deep crawling to verify orphan status can consume significant resources, requiring careful prioritization of verification efforts.
Custom user agent configuration helps ensure crawl results match search engine behavior rather than general web browsing patterns. Some orphan pages might be accessible to regular browsers but blocked from search engine crawlers through technical restrictions.
Crawl frequency adjustments accommodate different change patterns across site sections. High-velocity content areas might require daily orphan checks, while stable reference sections need only periodic verification.
Data integration and analysis workflows
Combining data from multiple sources requires standardized URL normalization to ensure accurate matching across systems. Inconsistent URL formatting often creates false positives in orphan detection systems.
Historical trend analysis helps distinguish permanent orphan pages from temporary disconnections caused by routine maintenance or system updates. This context improves decision-making about which pages require immediate attention.
Performance correlation analysis identifies patterns between orphan status and other SEO metrics. Understanding these relationships helps predict the business impact of orphan page problems before they fully manifest in rankings or traffic.
Automated reporting systems keep stakeholders informed about orphan page trends without requiring manual data compilation. However, these reports must focus on actionable insights rather than raw metrics to drive appropriate responses.
Advanced considerations for large-scale websites
Enterprise websites face unique orphan page challenges that don't apply to smaller properties. Scale amplifies both the frequency of orphan page emergence and the complexity of detection and resolution efforts.
Multi-domain and subdomain complications
Cross-domain link analysis becomes necessary when orphan pages exist on secondary domains or subdomains that should integrate with main website architecture. These distributed orphan pages often escape detection in standard single-domain audits.
Subdomain isolation can create functional orphan pages that technically have internal links but exist outside meaningful site architecture. These pages might maintain technical connectivity while suffering from practical abandonment.
International site management introduces additional complexity when orphan pages appear on country-specific domains or language variants. Global SEO strategies must account for orphan pages across all regional implementations.
Brand portfolio management requires coordinated orphan page strategies across multiple websites and properties. Orphan pages on subsidiary brand sites can affect overall domain authority distribution and competitive positioning.
Platform migration and restructuring challenges
Most often, orphan pages are caused by mistakes in site migrations, navigation changes, making migration planning crucial for orphan prevention. Enterprise migrations typically involve thousands of URLs, making manual verification impractical.
URL structure changes during platform migrations frequently create orphan pages when old internal links don't update properly to match new URL patterns. Automated link update systems must account for all possible internal link locations, including dynamic content and database-stored links.
Content management system changes can alter how internal links are generated and maintained, potentially creating systematic orphan page problems. Testing internal link functionality should be a core component of any CMS migration process.
Third-party integration updates might break internal linking systems that depend on external tools or services. Monitoring systems must detect these integration failures quickly to prevent widespread orphan page emergence.
Resource allocation and ROI optimization
Large-scale orphan page management requires significant resource investment in tools, systems, and personnel. ROI optimization ensures these investments focus on high-impact improvements rather than comprehensive but low-value fixes.
Triage systems help prioritize orphan page recovery based on potential traffic and conversion value. Not every orphan page justifies immediate attention, but identifying high-value targets prevents resources from being diluted across low-impact fixes.
Automation investment reduces long-term resource requirements for orphan page management. While initial automation setup requires significant investment, automated systems typically provide better coverage and consistency than manual processes.
Team training and skill development ensure that orphan page management capabilities remain current with evolving SEO best practices and technical requirements. This investment prevents knowledge gaps that can lead to recurring orphan page problems.
Measuring impact and optimizing recovery strategies
Effective orphan page management requires metrics that go beyond simple detection and resolution counts. Success measurement must demonstrate business value to justify ongoing investment in orphan page prevention and recovery.
Performance tracking methodologies
Traffic recovery analysis measures the organic search improvement attributable to orphan page reconnection. However, this analysis must account for seasonal trends, competitive changes, and other factors that might influence organic performance independent of orphan page status.
Ranking position monitoring tracks how reconnected orphan pages perform in search results over time. This data helps refine internal linking strategies and identify content types that recover most effectively from orphan status.
Conversion impact assessment determines whether recovered orphan pages contribute to business objectives beyond traffic generation. Pages that drive qualified leads or sales deserve higher recovery priority than those generating only informational traffic.
Crawl efficiency metrics evaluate how orphan page improvements affect overall site crawling and indexing performance. Reduced orphan page counts should correlate with more efficient crawl budget utilization across the entire domain.
Long-term optimization strategies
Set up a recurring crawl to catch any new unlinked pages in the future. Ongoing monitoring prevents orphan page problems from recurring while enabling continuous improvement of prevention systems.
Pattern analysis identifies recurring causes of orphan page emergence, enabling targeted prevention efforts. Understanding why orphan pages develop helps address root causes rather than just symptoms.
Performance benchmarking establishes baseline metrics for orphan page frequency and impact, enabling objective assessment of improvement efforts over time. These benchmarks also support resource allocation decisions for ongoing orphan page management.
Strategic evolution adapts orphan page management approaches as websites grow and change. What works for a 10,000-page site might not scale effectively to 100,000 pages, requiring ongoing strategy refinement.
Industry-specific orphan page considerations
Different industries face unique orphan page challenges based on their content types, business models, and regulatory requirements. Understanding these industry-specific factors helps optimize orphan page strategies for particular business contexts.
E-commerce and product catalog management
Product page orphaning frequently occurs during inventory management processes, seasonal catalog updates, or supplier relationship changes. These orphan pages often retain valuable SEO authority and customer reviews that justify recovery efforts even for discontinued products.
Category restructuring can create orphan pages when product categories are consolidated or reorganized. Maintaining appropriate internal links during these changes requires careful planning and execution to prevent temporary or permanent orphaning.
Promotional landing pages often become orphaned after campaigns end, but they might retain ranking value for branded terms or product-specific queries. Strategic decisions about maintaining or redirecting these pages affect long-term SEO performance.
Publishing and content-heavy websites
Editorial workflow changes can create orphan pages when content approval processes alter internal linking patterns. Large publishing operations require systematic approaches to ensure new content integrates properly with existing site architecture.
Archive management presents ongoing orphan page challenges as older content becomes less relevant but might retain search engine value. Balancing content freshness against historical SEO authority requires nuanced decision-making.
Author and contributor pages can become orphaned when staff changes occur or contributor relationships end. These pages often accumulate authority through byline links and external references, making their orphan status particularly problematic.
Service-based and professional websites
Case study and project showcase pages might become orphaned when client relationships end or project details become confidential. However, these pages often demonstrate expertise and attract prospects, justifying efforts to maintain their search visibility.
Resource libraries and knowledge bases can develop orphan pages when information architecture changes or content management systems are updated. These educational materials often attract high-quality traffic and support thought leadership positioning.
Location-specific pages for service businesses might become orphaned during expansion or contraction of service areas. Geographic SEO strategies must account for these changes to maintain local search visibility.
Emerging trends and future considerations
Orphan page management continues evolving as search engines update their crawling and ranking algorithms. SEO professionals must anticipate these changes to maintain effective orphan page strategies.
Algorithm updates and crawling changes
Machine learning improvements in search engine crawling might reduce the SEO impact of orphan pages if crawlers become better at discovering content through alternative pathways. However, internal links will likely remain the primary discovery mechanism for the foreseeable future.
Mobile-first indexing considerations affect how orphan pages are detected and prioritized, particularly when mobile and desktop site architectures differ significantly. Mobile orphan page detection requires specialized approaches that account for responsive design implementations.
Core Web Vitals and page experience factors might influence how search engines treat orphan pages, particularly if these pages have performance issues that compound their link isolation problems.
Technology integration opportunities
Artificial intelligence applications could automate orphan page detection and recovery recommendations, reducing the manual effort required for large-scale orphan page management. However, human oversight remains essential for strategic decisions about which pages deserve recovery.
Content management system integration improvements might eliminate many common causes of orphan page emergence by building better internal linking automation into publishing workflows.
API development enables custom orphan page management solutions that integrate with existing SEO toolchains and business processes. These integrations support more sophisticated approaches to prevention and recovery than standalone tools typically provide.
The evolution of link building strategies also impacts orphan page management. As research shows that 73% of link builders focus on relationship-based approaches, internal linking strategies must evolve to support these external link acquisition efforts. Well-connected internal pages provide better targets for external link building campaigns than orphaned alternatives.
Understanding orphan pages becomes increasingly important as websites grow more complex and competitive pressures intensify. The pages you can't find might be costing you more traffic and authority than you realize, making systematic orphan page management an essential component of enterprise SEO success.
Professional SEO teams who master advanced orphan page detection and recovery strategies gain significant competitive advantages through better resource utilization and more comprehensive content optimization. The investment in proper systems and processes pays dividends through improved crawl efficiency, better internal link equity distribution, and enhanced overall organic performance.
For organizations serious about maximizing their SEO potential, professional link building services that understand both internal and external link optimization can provide the expertise needed to implement comprehensive orphan page management alongside broader link acquisition strategies.

 By
By